Difference between revisions of "3D Reslicing using COMKAT image tool (basic)"
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | ====Example ( Cardiac-PET )==== | + | ====Example (Cardiac-PET)==== |
First, let's use the approach I to obtain a new slice. | First, let's use the approach I to obtain a new slice. | ||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | ||
To obtain a new slice, we need to specific the number of rows and columns in the new image | To obtain a new slice, we need to specific the number of rows and columns in the new image | ||
Nc = 370; % # of columns | Nc = 370; % # of columns | ||
Nr = 370; % # of rows | Nr = 370; % # of rows | ||
| − | Specify the sampling pixel size of | + | Create the indices of each voxel |
| + | [i, j] = meshgrid(0 : Nc-1, 0 : Nr-1); | ||
| + | ij = [c(:)’ ; r(:)’]; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specify the sampling pixel size and the position of sampling plane | ||
pixelSpacingOrg = [1.5501; 1.5501]; % Set pixel size (mm) | pixelSpacingOrg = [1.5501; 1.5501]; % Set pixel size (mm) | ||
| + | |||
| + | planePosOrg = [-0.7751; -0.7751; 88.0000]; % Set the reslicing plane location | ||
| + | |||
| + | Set the orientation matrix | ||
| + | |||
| + | orientationInput = [1, 0; | ||
| + | 0, 1; | ||
| + | 0, 0]; | ||
| + | |||
| + | Now, we're going to calculate physical location (mm) of voxels in the desired image | ||
| + | xyz = orientationInput * pixelSpacingOrg* ij + repmat(planePosOrg ,1 , Nr * Nc); | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | After obtaining the physical location, we need to calculate the indices of each voxel in the original volume space. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Use the inverse mapping method to calculate the indices in the original image volume | ||
| + | |||
| + | We need to obtain the original pixel size, orientation, and image position matrices for the inverse mapping | ||
| + | |||
| + | You can specify your image information. Here we use function get() to obtain the information we need from the IVD | ||
| + | |||
| + | [ny, nx, nz, nf] = get(ivd, 'VolumeDimension'); | ||
| + | pixDim = get(ivd, 'PixelSpacing'); | ||
| + | vol_Uspacing = pixDim(2); | ||
| + | vol_Vspacing = pixDim(1); | ||
| + | vol_Wspacing = pixDim(3); | ||
| + | |||
| + | vol_pos = get(ivd, 'ImagePositionPatient'); | ||
| + | vol_orient = get(ivd, 'ImageOrientationPatient'); | ||
| + | |||
| + | Therefore, the inverse mapping can be done as follow: | ||
| + | |||
| + | uvw = diag([1./vol_Uspacing 1./vol_Vspacing 1./vol_Wspacing]) * inv(vol_orient) * ( xyz - repmat(vol_pos, 1, Nr * Nc) ); | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to use sliceVolume() to do the interpolation, we need to separate uvw in three separate matrices. | ||
| + | u = ( reshape(uvw(1,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; | ||
| + | v = ( reshape(uvw(2,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; | ||
| + | w = ( reshape(uvw(3,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Note: the indices in original image volume are defined to start from 1. So after performing the inverse mapping, the indices need to be add by 1. | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | ||
orientationInput = [1, 0, 0; | orientationInput = [1, 0, 0; | ||
Revision as of 20:59, 13 August 2012
Reslicing 3D image volume using COMKAT image tool (basic)
Overview
Reslicing a 3D (or 3D vs time) image dataset can be accomplished using various components of COMKAT including the function sliceVolume() which is a method of ImageVolumeData. This example explains how to create a 2D image by slicing from a volume at a position, plane orientation, and magnification specified by the user. The approach is to load the image volume dataset into an instance of an ImageVolumeData (abbreviated IVD) object and to use the sliceVolume() method.
Background
sliceVolume() is a mex-file written in c with an interface to MATLAB that makes the operation particularly efficient. COMKATImageTool uses sliceVolume() and you can use it too.
Approach I. Demonstrate the method for coordinate transformations
Create an instance of an IVD and load it with an image volume.
ivd = ImageVolumeData(); % create an instance of an ImageVolumeData object ivd = read_DICOM(ivd, pathName, fileName); % load volume into an instance of IVD object;
Create lists of indices of all pixels in the 2D slice (rectangular grid) that we are creating
[i, j] = meshgrid(0 : Nc-1, 0 : Nr-1); % i and j will be 2D arrays, meshgrid is a function built into MATLAB ij = [c(:)’ ; r(:)’]; % make matrix, each column corresponding to a single pixel in the slice we are creating
The first and second rows of ij are the indices corresponding to column and row indices of all voxels in the desired slice. So the dimension of ij is 3 x ( # of desired voxels ).
For example, the first column of ij could be [ 0 ; 0 ] ; the second column could be [ 0 ; 1 ] , etc.
Compute the physical x,y,z locations, in mm, from pixel indices according to the DICOM coordinate system ref [1] p. 275.
This is a two-step process. The first step is to compute the coordinate transformation matrix. Note that pixel spacing/zoom, orientation, and position for the slice are specified in the transformation matrix.
M = ( Insert the method for generating the transformation matrix );
The second step is to use the transformation matrix to calculate the physical (mm) location of each pixel in the desired slice
xyz = M * ij; % xyz is a matrix consisted of three rows the physical x, y, and z location (m) of all the desired voxels. The dimension of xyz is 3 x ( # of desired voxels ).
These xyz locations are the same as those in the image volume that is being sliced to make the 2D image. From these xyz locations, we find the corresponding 3D indices, (u,v,w), into the volume. This uses the transformation matrix for the volume, Mhat, that relates the indices to the xyz physical location. This is analogous to M used for the desired slice but here the pixel spacing, orientation, and position indicate how the volume data are stored.
Specify the matrix for reverse mapping ( index space of the original image volume (uvw) --> xyz )
Mhat = ( Insert the method for generate the mapping);
Calculate voxel indcies into the volume corresponding to xyz physical location
uvw = inv( Mhat ) * xyz; % uvw is the matrices consisted of the indices in the domain of the original volume
uvw is a matrix consisted of three rows corresponding to row, column, and plane indices of the original volume data. The dimension of uvw is identical of that of xyz.
Separate uvw into the components
u = ( row indices in the domain of original of volume data );
v = ( column indices in the domain of original of volume data );
w = ( plane indices in the domain of original of volume data );
Therefore, the u, v, w are the first, second, and third rows of uvw.
Use sliceVolume() to interpolate the slice
slice = sliceVolume(idv, v, u, w, rawbackgroundPixelValue , 'linear');
backgroundPixelValue is a value that used for the interpolation when it is nothing there for calculating the interpolation value. The value is a unscaled raw background value of images.
In gerneral, rawbackgroundPixelValue = (scaled_pixel_value - rescale_intercept) / (rescale_slope) ;
e.g. For PET, the scaled background value is usually zero.
==> rawbackgroundPixelValue = ( 0 - rescale_intercept) / rescale_slope ;
So rawbackgroundPixelValue can be calculated as follows:
s = get( ivd, 'VolumeFrameBufferScaleFactor'); % rescale_slope o = get( ivd, 'VolumeFrameBufferRescaleIntercept'); % rescale_intercept rawbackgroundPixelValue = - o / s;
Display new slice
figure, imagesc(slice); axis image % isotropic
Approach II. Use coordinateGen() to do the coordinate transformation
- This should create same result as approach I but require fewer lines of coding since coordinateGen() does most things that are needed.
Read the image volume into an ImageVolumeData object
ivd = ( Insert the method for reading data );
Use coordinateGen() to generate uvw
[u, v, w] = coordinateGen(ivd, Nc, Nr, pixelSpacing, planePos, orientation); % Input the desired pixelSpacing, planePos and orientation matrices
Use sliceVolume() to interpolate
slice = sliceVolume(idv, v, u, w, backgroundPixelValue, 'linear');
Display slice
figure, imagesc(slice); axis image % isotropic
Example (Cardiac-PET)
First, let's use the approach I to obtain a new slice.
ivd = (read data into IVD);
To obtain a new slice, we need to specific the number of rows and columns in the new image
Nc = 370; % # of columns Nr = 370; % # of rows
Create the indices of each voxel
[i, j] = meshgrid(0 : Nc-1, 0 : Nr-1);
ij = [c(:)’ ; r(:)’];
Specify the sampling pixel size and the position of sampling plane
pixelSpacingOrg = [1.5501; 1.5501]; % Set pixel size (mm) planePosOrg = [-0.7751; -0.7751; 88.0000]; % Set the reslicing plane location
Set the orientation matrix
orientationInput = [1, 0;
0, 1;
0, 0];
Now, we're going to calculate physical location (mm) of voxels in the desired image
xyz = orientationInput * pixelSpacingOrg* ij + repmat(planePosOrg ,1 , Nr * Nc);
After obtaining the physical location, we need to calculate the indices of each voxel in the original volume space.
Use the inverse mapping method to calculate the indices in the original image volume
We need to obtain the original pixel size, orientation, and image position matrices for the inverse mapping
You can specify your image information. Here we use function get() to obtain the information we need from the IVD
[ny, nx, nz, nf] = get(ivd, 'VolumeDimension'); pixDim = get(ivd, 'PixelSpacing'); vol_Uspacing = pixDim(2); vol_Vspacing = pixDim(1); vol_Wspacing = pixDim(3);
vol_pos = get(ivd, 'ImagePositionPatient'); vol_orient = get(ivd, 'ImageOrientationPatient');
Therefore, the inverse mapping can be done as follow:
uvw = diag([1./vol_Uspacing 1./vol_Vspacing 1./vol_Wspacing]) * inv(vol_orient) * ( xyz - repmat(vol_pos, 1, Nr * Nc) );
In order to use sliceVolume() to do the interpolation, we need to separate uvw in three separate matrices.
u = ( reshape(uvw(1,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; v = ( reshape(uvw(2,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; w = ( reshape(uvw(3,:), [Nr, Nc]) ) + 1; * Note: the indices in original image volume are defined to start from 1. So after performing the inverse mapping, the indices need to be add by 1.
orientationInput = [1, 0, 0;
0, 1, 0;
0, 0, 1]; % Set the orientation matrix
% Set background value for interpolation
s = get(ivd, 'VolumeFrameBufferScaleFactor');
o = get(ivd, 'VolumeFrameBufferRescaleIntercept');
rawBackgroundPixelValue = -o/s;
% Generate new coordinate for slicing
[u, v, w] = coordinateGen(ivd, Nc, Nr, pixelSpacingOrg, planePosOrg, orientationInput);
% Slice interpolation
slice = sliceVolume(ivd, v , u , w, rawBackgroundPixelValue,'linear');
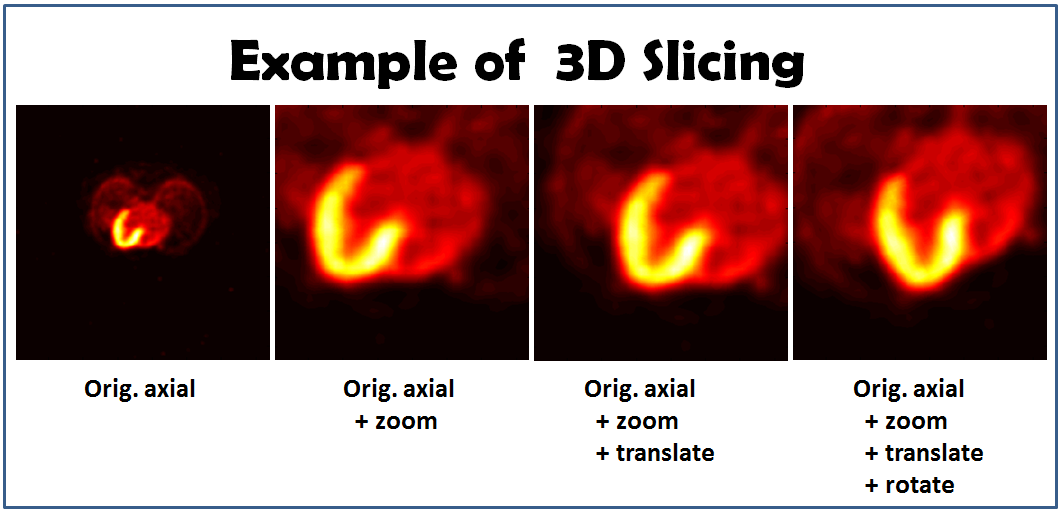
figure, imagesc(slice), axis image, colormap(hot) % show org image
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%% Zoom %%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% zoomFactor = 3; % set zoom factor pixelSpacing = pixelSpacingOrg / zoomFactor; % adjust pixel size % after zooming you may need to translate the image center, or you may see nothing originalFOV = [Nc; Nr; 0] .* pixelSpacingOrg; % calculate the original FOV zoomShift = originalFOV / 2 * (zoomFactor - 1) / zoomFactor ; planePos = planePosOrg + zoomShift ; % Generate new slice [u, v, w] = coordinateGen(ivd, Nc, Nr, pixelSpacing, planePos, orientationInput); slice = sliceVolume(ivd, v , u , w, rawBackgroundPixelValue,'linear'); figure, imagesc(slice), axis image, colormap(hot) % show org +zoom
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%% Translation %%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% transMat = [-35.0; -5; 0]; % set translation matrix planePosTrans = planePos + transMat; % calculate new plane position % Generate new slice [u, v, w] = coordinateGen(ivd, Nc, Nr, pixelSpacing, planePosTrans, orientationInput); slice = sliceVolume(ivd, v , u , w, rawBackgroundPixelValue,'linear'); figure, imagesc(slice), axis image, colormap(hot) % show org +zoom+translation
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%%%% Rotation %%%%
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
rotAngle = 25/180*pi; % rotate 20 degree
orientationInputRot = [ cos(rotAngle), -sin(rotAngle), 0;
sin(rotAngle), cos(rotAngle), 0;
0, 0, 1]; % rotate the orientation matrix (counter-clockwise)
% after rotation, we adjust the center of the rotated image
newFOV = [Nc; Nr; 0] .* pixelSpacing; % calculate new FOV after zooming
transMat2 = orientationInputRot * ( newFOV / 2 ) - newFOV / 2; % calculate the translation of the center after rotation
planePosTrans2 = planePosTrans - transMat2; % translate the rotated image center (backward)
% Generate new slice
[u, v, w] = coordinateGen(ivd, Nc, Nr, pixelSpacing, planePosTrans2, orientationInputRot);
slice = sliceVolume(ivd, v , u , w, rawBackgroundPixelValue,'linear');
figure, imagesc(slice), axis image, colormap(hot) % show org+zoom+translate+rotate
The slicing images may look like this: