Difference between revisions of "Support:Documents:Examples:Model Corrected Input Function"
| (7 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
===Overview=== | ===Overview=== | ||
| − | For | + | For <sup>18</sup>F-FDG PET studies, the estimation of kinetic rate constants required knowledge of the input function (i.e., <sup>18</sup>F-FDG plasma time activity curve). The standard method to determine the input function is to measure 18F-FDG activity concentration in the arterial blood. However, this invasive procedure is limited by the small size of blood vessels and the limited blood volume in small animal imaging. For humans, we prefer to avoid arterial blood sampling for reasons of safety, discomfort, and inconvenience. One alternative way is to estimate the input function non-invasively. One of non-invasive methods is image-derived input functions (IDIFs), which estimate input function from a region of interest (ROI) within the ventricular cavity. However, due to the limited spatial resolution and the cardiac and respiratory motion, cross-contamination from surrounding tissues to vascular structures affects the accuracy of estimated input function. To solve these problems, [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18344438?ordinalpos=1&itool=EntrezSystem2.PEntrez.Pubmed.Pubmed_ResultsPanel.Pubmed_DefaultReportPanel.Pubmed_RVDocSum Fang] proposed a model-corrected input function (MCIF), which used simultaneous estimation to correct the spillover and partial volume effect for IDIFs. |
==Example of Estimating Input Function Using MCIF== | ==Example of Estimating Input Function Using MCIF== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Here is an example of COMKAT GUI for estimating kinetic rate constants, and the MCIF method is used to estimate input function. | Here is an example of COMKAT GUI for estimating kinetic rate constants, and the MCIF method is used to estimate input function. | ||
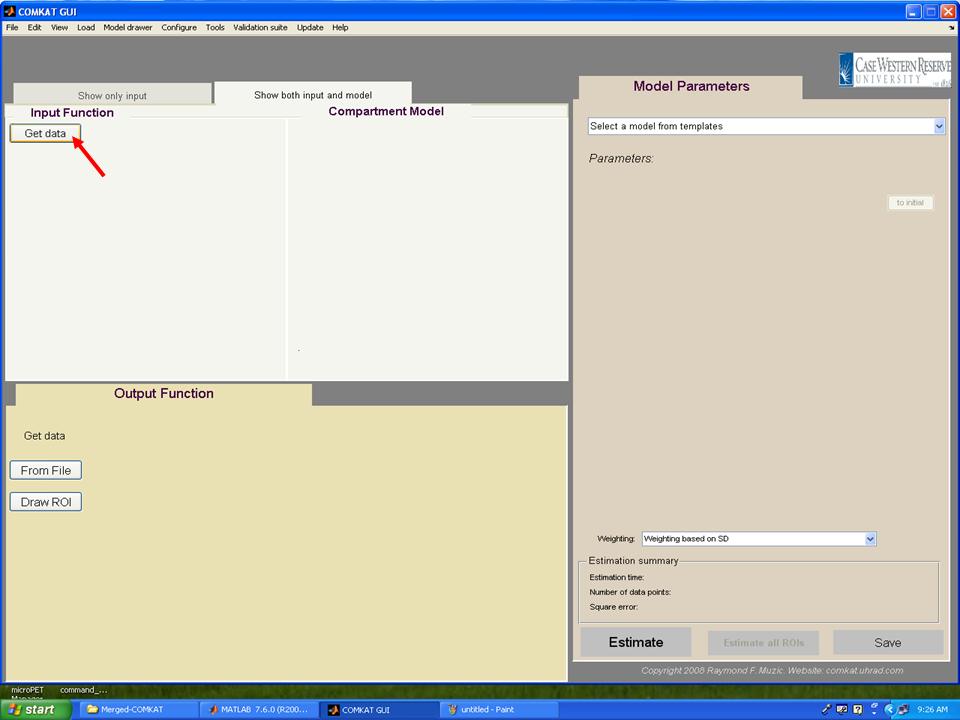
| − | Step 1. Type "comkat" in Matlab commandwindow and "COMKAT_GUI" GUI (below figure) should be started. | + | '''Step 1.''' Type "comkat" in Matlab commandwindow and "COMKAT_GUI" GUI (below figure) should be started. |
[[Image:fig1.1.jpg]] | [[Image:fig1.1.jpg]] | ||
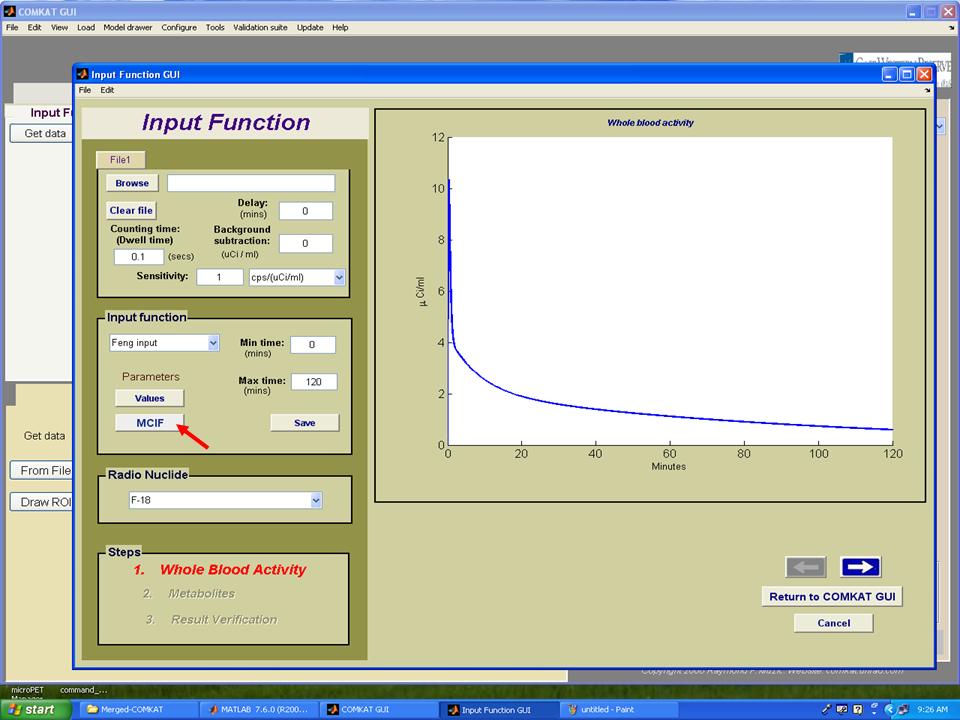
| − | Step 2. Hit 'Get data' button in "COMKAT_GUI" and "Input Function GUI" (below figure) shoud be started. | + | '''Step 2.''' Hit 'Get data' button in "COMKAT_GUI" and "Input Function GUI" (below figure) shoud be started. |
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
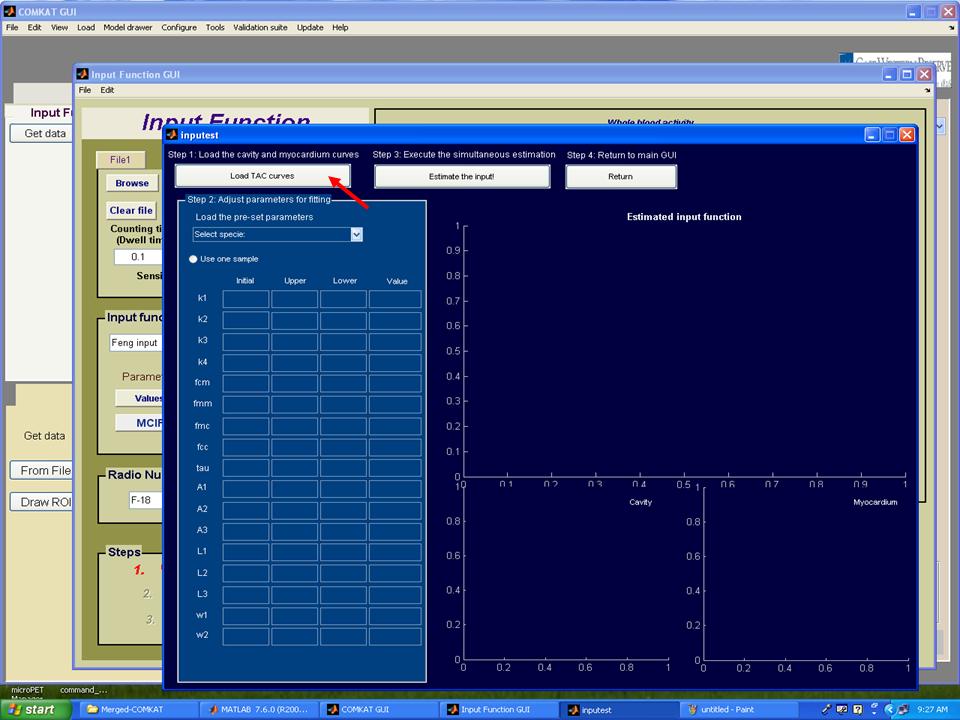
| − | Step 3. Hit 'MCIF' button in "Input Function GUI" and "inputest" GUI (below figure) shoud be started. | + | '''Step 3.''' Hit 'MCIF' button in "Input Function GUI" and "inputest" GUI (below figure) shoud be started. |
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
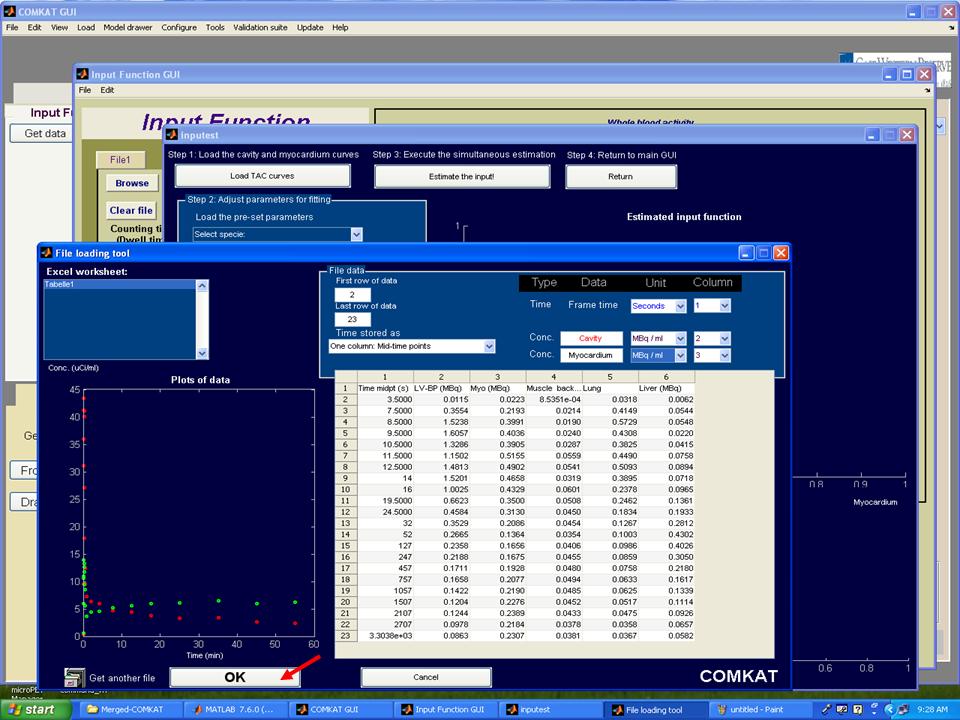
| − | Step 4. Hit 'Load TAC curves' button in "inputest" GUI and "File loading tool" GUI (below figure) should be started. Then, choose concentrations of cavity and myocardium from the file user loaded and set units that user defined. Hit 'OK' button to return to "inputest" GUI. | + | '''Step 4.''' Hit 'Load TAC curves' button in "inputest" GUI and "File loading tool" GUI (below figure) should be started. Then, choose concentrations of cavity and myocardium from the file user loaded and set units that user defined. Hit 'OK' button to return to "inputest" GUI. |
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
| − | Step 5. Now, the TAC curves for cavity and myocardium should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure). Then, hit 'Load the pre-set parameters' to choose the animal model user used. Note: pre-set parameters may change with different studies and user should try different initial, upper and lower values. | + | '''Step 5.''' Now, the TAC curves for cavity and myocardium should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure). Then, hit 'Load the pre-set parameters' to choose the animal model user used. Note: pre-set parameters may change with different studies and user should try different initial, upper and lower values. |
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| − | Step 6. Hit 'Estimate the input' button to start the estimation of parameters. Note: please wait several minutes until the estimation process completed. | + | '''Step 6.''' Hit 'Estimate the input' button to start the estimation of parameters. Note: please wait several minutes until the estimation process completed. |
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
| − | Step 7. As the estimation process completed, the TAC curve for estimated input function should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure) and the estimated parameters should in the column 'Value'. Then, hit 'Return' button to return to "Input Function GUI". | + | '''Step 7.''' As the estimation process is completed, the TAC curve for estimated input function should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure) and the estimated parameters should in the column 'Value'. Then, hit 'Return' button to return to "Input Function GUI". |
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
| − | Step 8. The TAC curve for whole blood activity should appear in "Input Function GUI". Note: hit 'Values' to see estimated parameters that define the input function. Hit the arrow to the next step. | + | '''Step 8.''' The TAC curve for whole blood activity should appear in "Input Function GUI". Note: hit 'Values' to see estimated parameters that define the input function. Hit the arrow to the next step. Users could save these estimated parameters in the step 15. |
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
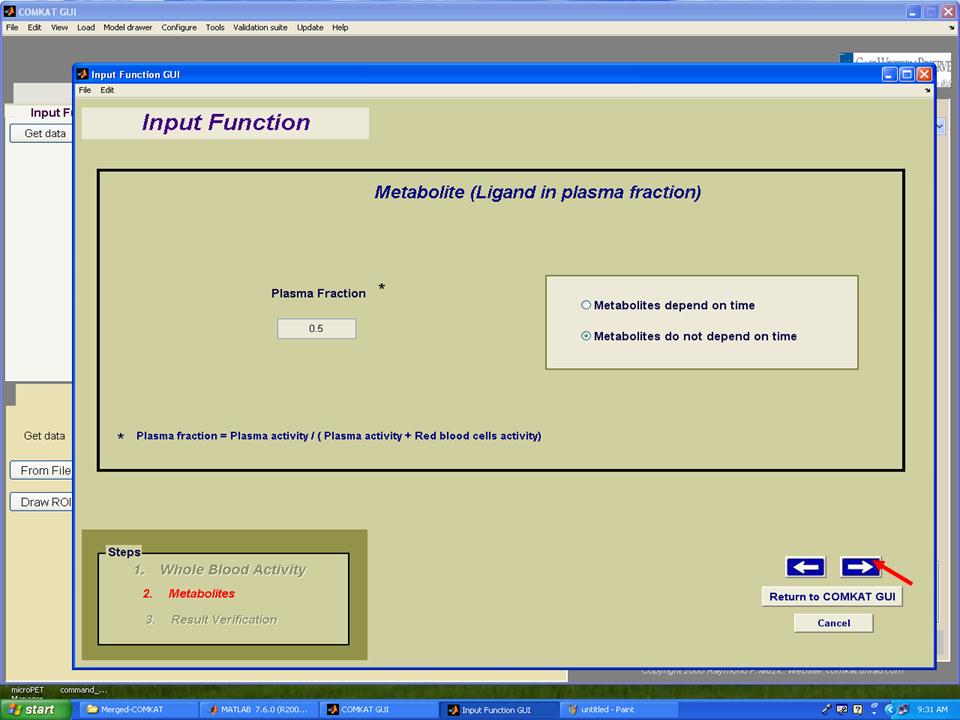
| − | Step 9. Set plasma fraction and then hit the arrow to the next step. | + | '''Step 9.''' Set plasma fraction and then hit the arrow to the next step. |
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
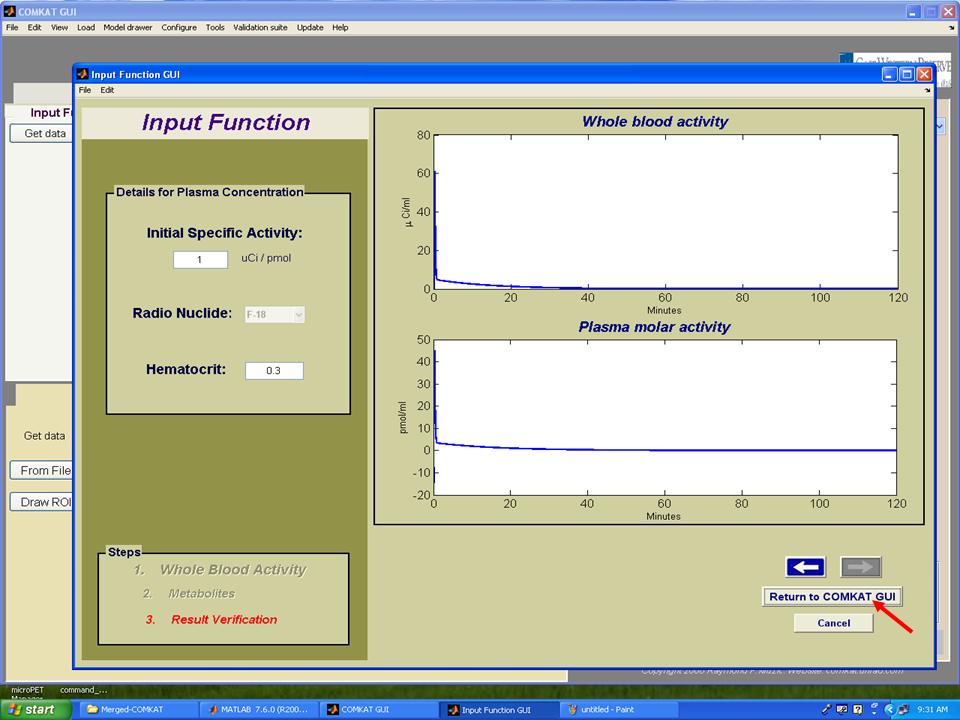
| − | Step 10. Set initial specific activity and hematocrit for producing TAC curve for plasma and then hit 'Return to COMKAT GUI' button to return to "COMKAT GUI". | + | '''Step 10.''' Set initial specific activity and hematocrit for producing TAC curve for plasma and then hit 'Return to COMKAT GUI' button to return to "COMKAT GUI". |
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
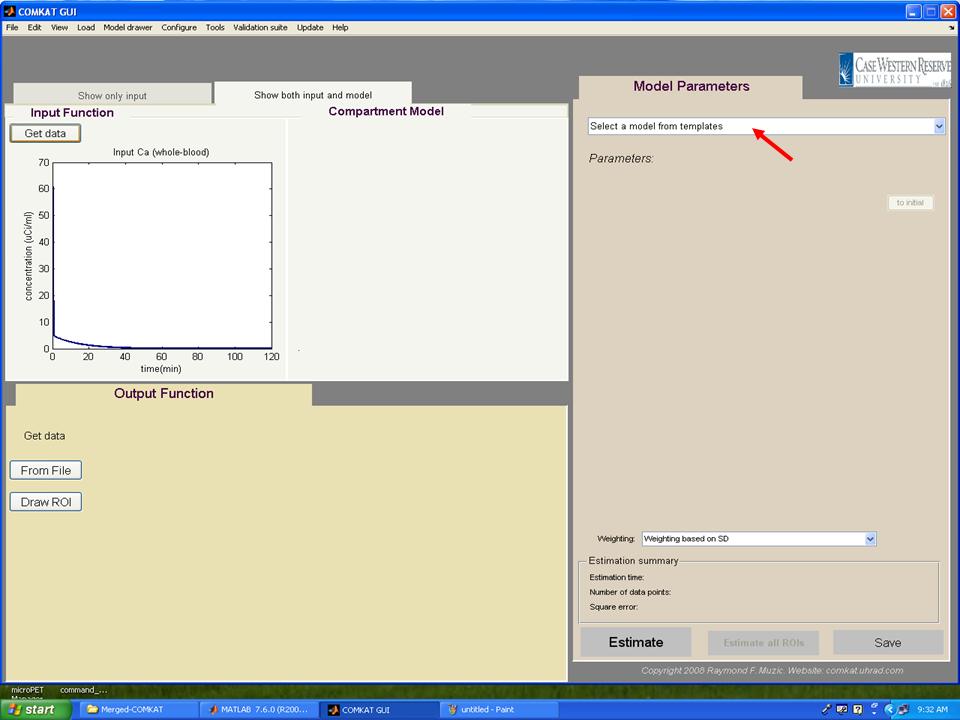
| − | Step 11. The TAC curve for whole blood should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Select a model from templates' to choose the kinetic model. | + | '''Step 11.''' The TAC curve for whole blood should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Select a model from templates' button to choose the kinetic model. |
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
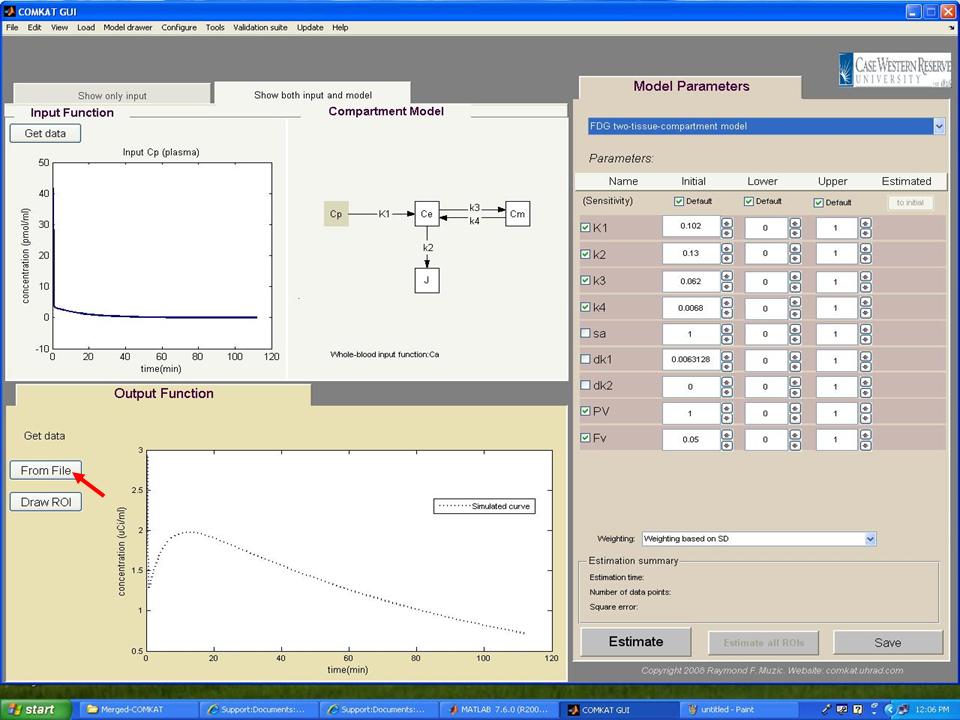
| − | Step 12. In "COMKAT GUI" (below figure), the initial, upper and lower kinetic rate constants for the model should appear in the right side of the figure. Then hit 'From file' or 'Draw ROI' button to load output function. | + | '''Step 12.''' In "COMKAT GUI" (below figure), the initial, upper and lower kinetic rate constants for the model should appear in the right side of the figure. Then hit 'From file' or 'Draw ROI' button to load output function. |
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
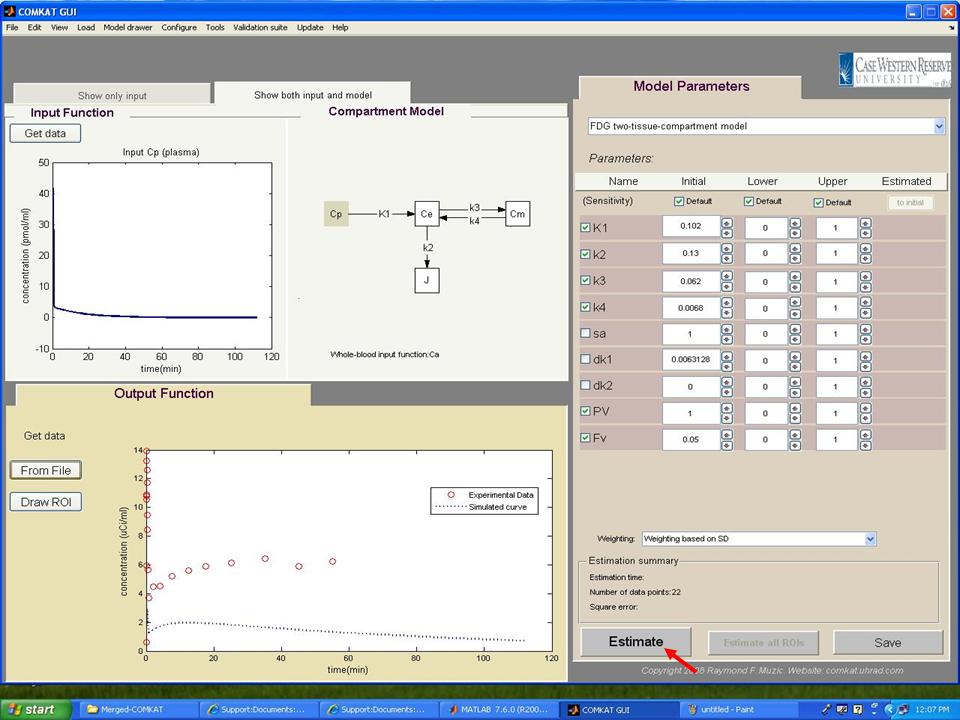
| − | Step 13. After loading output function, the TAC curve (Experimental Data: red circle) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Estimate' button to start the estimation of parameters. | + | '''Step 13.''' After loading output function, the TAC curve (Experimental Data: red circle) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Estimate' button to start the estimation of parameters. |
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
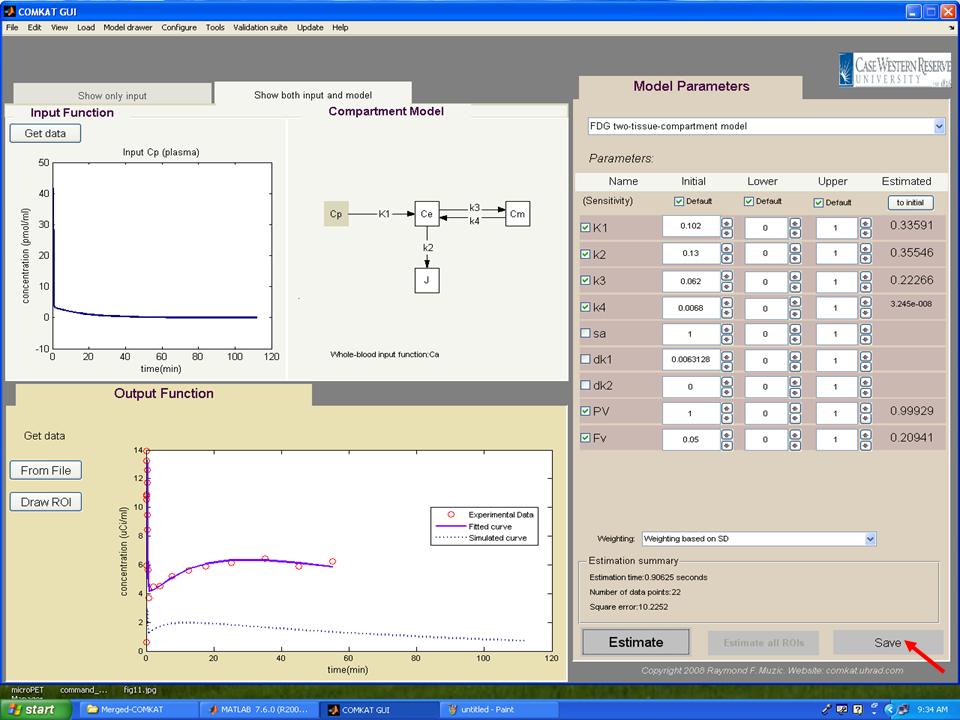
| − | Step 14. After the estimation process, the TAC curve (Fitting Curve: blue line) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure) and estimated parameters are in the right side of the figure. Then, hit 'Save' button to save results. | + | '''Step 14.''' After the estimation process, the TAC curve (Fitting Curve: blue line) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure) and estimated parameters are in the right side of the figure. Then, hit 'Save' button to save results. |
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
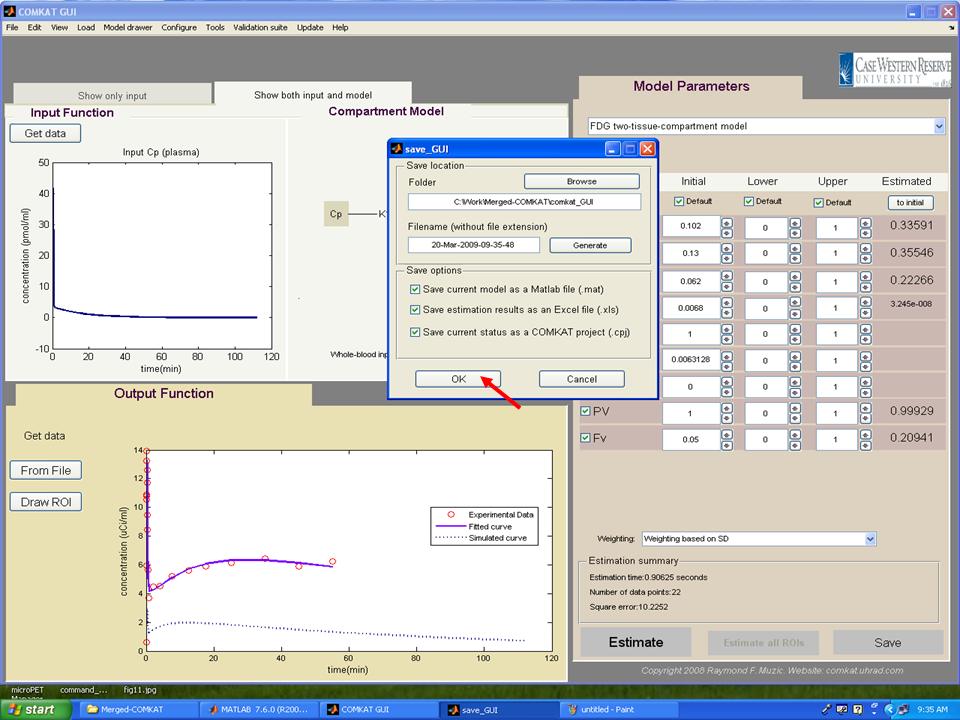
| − | Step 15. In "save_GUI", user can save results as a Matlab file, an Excel file or a COMKAT project in the folder. More details about COMKAT GUI can be found in [http://comkat.case.edu/comkat/comkat_wiki/index.php?title=Support:Documents:Manual:COMKAT_GUI this document.] | + | '''Step 15.''' In "save_GUI", user can save results as a Matlab file, an Excel file or a COMKAT project in the folder. More details about COMKAT GUI can be found in [http://comkat.case.edu/comkat/comkat_wiki/index.php?title=Support:Documents:Manual:COMKAT_GUI this document.] |
[[Image:fig1.14.jpg]] | [[Image:fig1.14.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:15, 26 March 2009
Model-Corrected Input Function
Overview
For 18F-FDG PET studies, the estimation of kinetic rate constants required knowledge of the input function (i.e., 18F-FDG plasma time activity curve). The standard method to determine the input function is to measure 18F-FDG activity concentration in the arterial blood. However, this invasive procedure is limited by the small size of blood vessels and the limited blood volume in small animal imaging. For humans, we prefer to avoid arterial blood sampling for reasons of safety, discomfort, and inconvenience. One alternative way is to estimate the input function non-invasively. One of non-invasive methods is image-derived input functions (IDIFs), which estimate input function from a region of interest (ROI) within the ventricular cavity. However, due to the limited spatial resolution and the cardiac and respiratory motion, cross-contamination from surrounding tissues to vascular structures affects the accuracy of estimated input function. To solve these problems, Fang proposed a model-corrected input function (MCIF), which used simultaneous estimation to correct the spillover and partial volume effect for IDIFs.
Example of Estimating Input Function Using MCIF
Here is an example of COMKAT GUI for estimating kinetic rate constants, and the MCIF method is used to estimate input function.
Step 1. Type "comkat" in Matlab commandwindow and "COMKAT_GUI" GUI (below figure) should be started.
Step 2. Hit 'Get data' button in "COMKAT_GUI" and "Input Function GUI" (below figure) shoud be started.
Step 3. Hit 'MCIF' button in "Input Function GUI" and "inputest" GUI (below figure) shoud be started.
Step 4. Hit 'Load TAC curves' button in "inputest" GUI and "File loading tool" GUI (below figure) should be started. Then, choose concentrations of cavity and myocardium from the file user loaded and set units that user defined. Hit 'OK' button to return to "inputest" GUI.
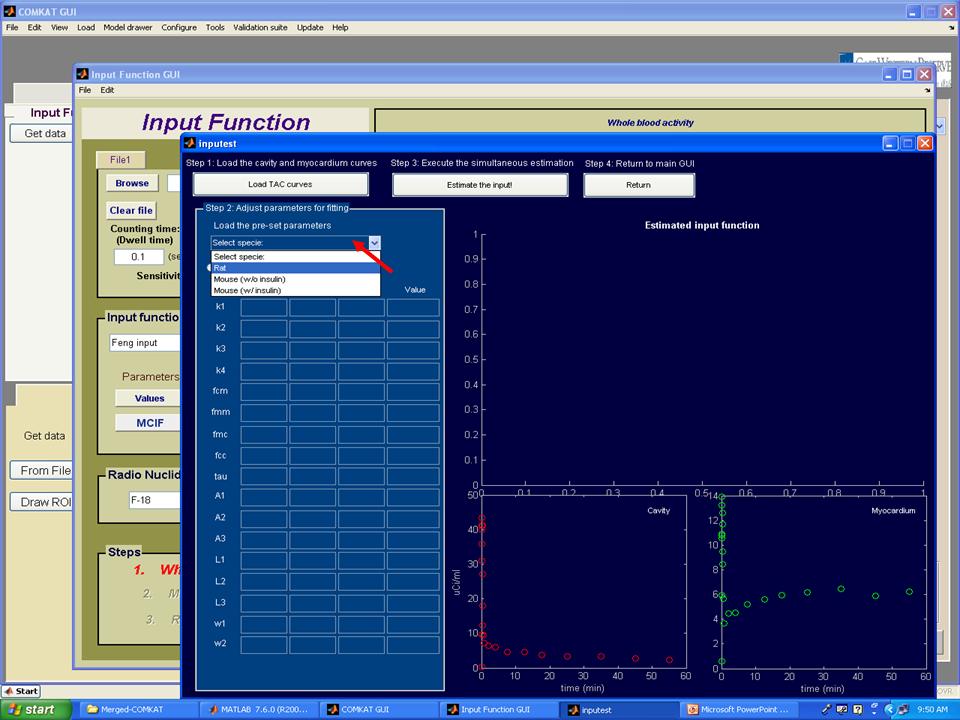
Step 5. Now, the TAC curves for cavity and myocardium should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure). Then, hit 'Load the pre-set parameters' to choose the animal model user used. Note: pre-set parameters may change with different studies and user should try different initial, upper and lower values.
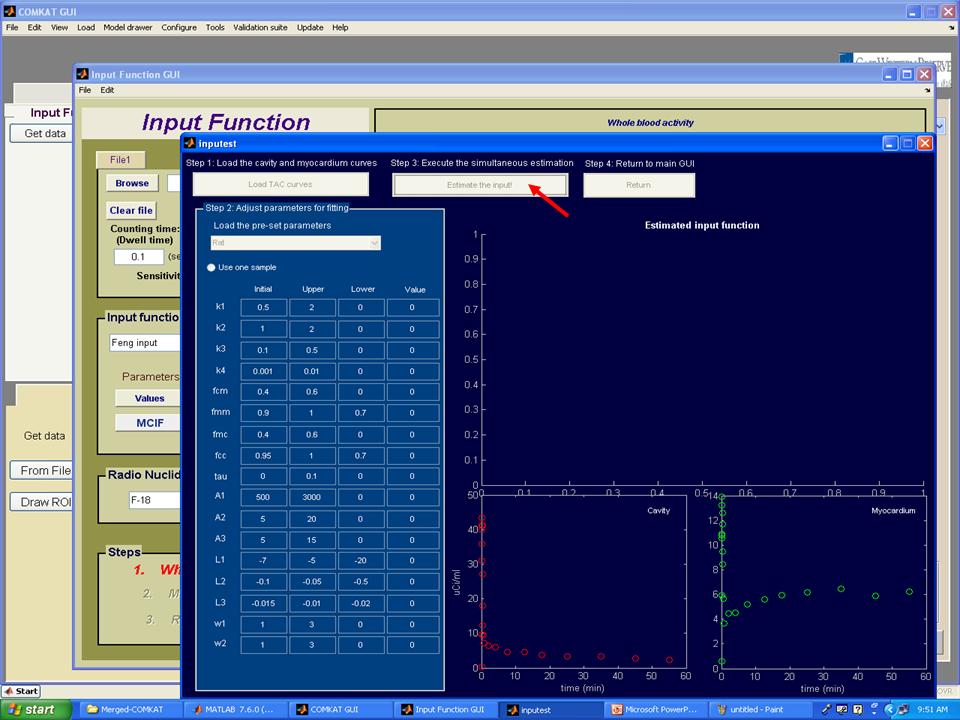
Step 6. Hit 'Estimate the input' button to start the estimation of parameters. Note: please wait several minutes until the estimation process completed.
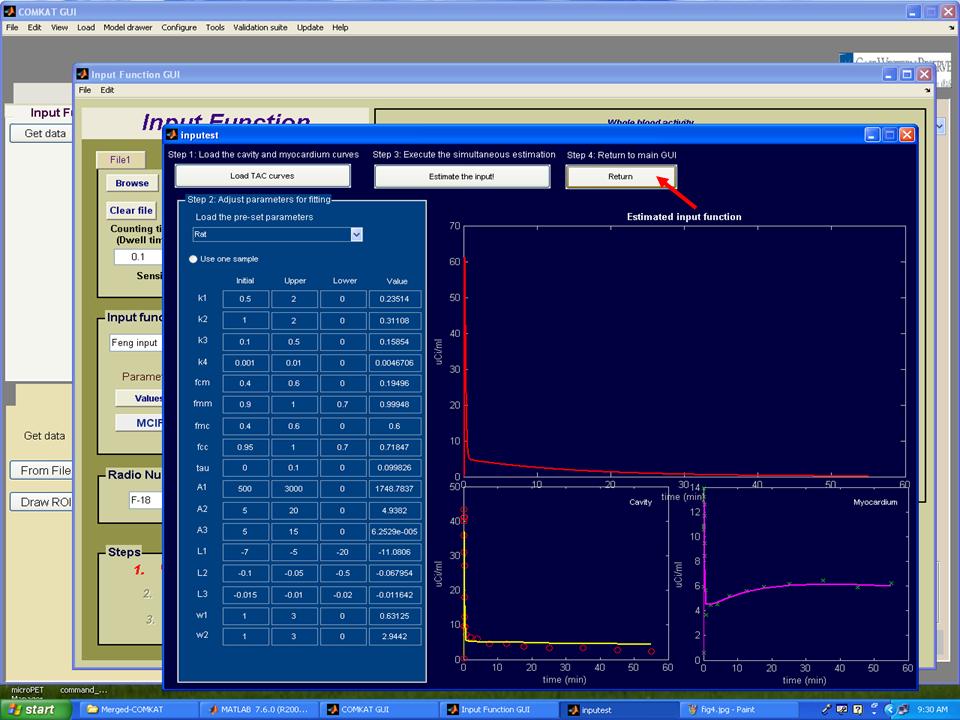
Step 7. As the estimation process is completed, the TAC curve for estimated input function should appear in "inputest" GUI (below figure) and the estimated parameters should in the column 'Value'. Then, hit 'Return' button to return to "Input Function GUI".
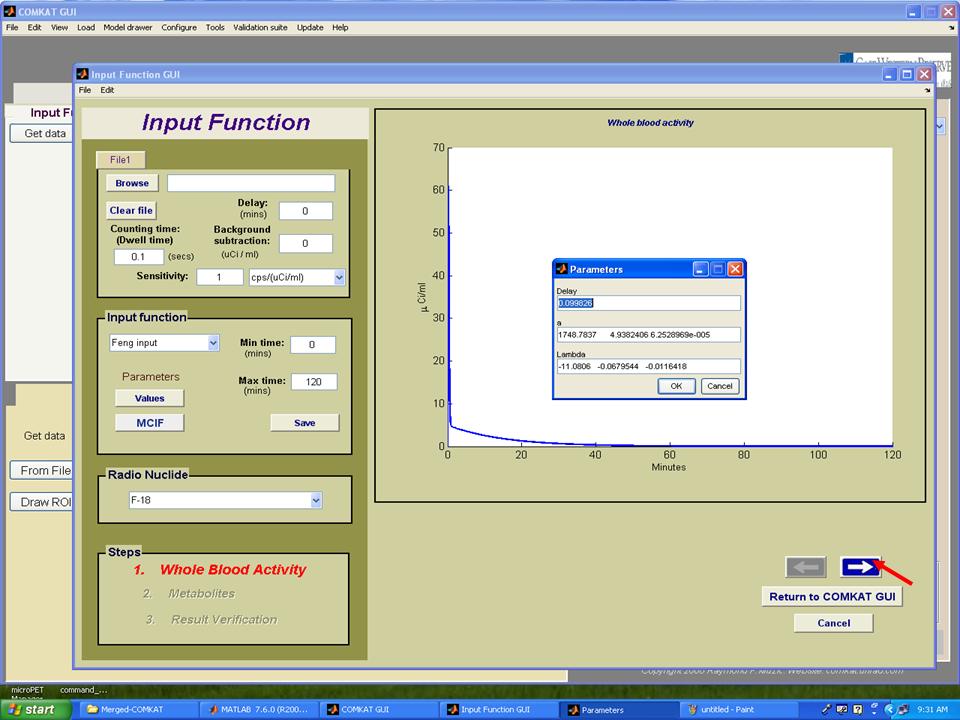
Step 8. The TAC curve for whole blood activity should appear in "Input Function GUI". Note: hit 'Values' to see estimated parameters that define the input function. Hit the arrow to the next step. Users could save these estimated parameters in the step 15.
Step 9. Set plasma fraction and then hit the arrow to the next step.
Step 10. Set initial specific activity and hematocrit for producing TAC curve for plasma and then hit 'Return to COMKAT GUI' button to return to "COMKAT GUI".
Step 11. The TAC curve for whole blood should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Select a model from templates' button to choose the kinetic model.
Step 12. In "COMKAT GUI" (below figure), the initial, upper and lower kinetic rate constants for the model should appear in the right side of the figure. Then hit 'From file' or 'Draw ROI' button to load output function.
Step 13. After loading output function, the TAC curve (Experimental Data: red circle) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure). Then, hit 'Estimate' button to start the estimation of parameters.
Step 14. After the estimation process, the TAC curve (Fitting Curve: blue line) should appear in "COMKAT GUI" (below figure) and estimated parameters are in the right side of the figure. Then, hit 'Save' button to save results.
Step 15. In "save_GUI", user can save results as a Matlab file, an Excel file or a COMKAT project in the folder. More details about COMKAT GUI can be found in this document.